中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (22): 3530-3535.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1279
• 纳米生物材料 nanobiomaterials • 上一篇 下一篇
纳米羟基磷灰石/胶原/聚乳酸新型可吸收材料的短期生物安全性
高 黎1,王书岩1,王 蕊1,许永华1,高静静1,张 丽2,刘文涛2
- 1郑州大学第一附属医院儿童口腔科,河南省郑州市 450001;2郑州大学材料科学与工程学院,河南省郑州市 450001
Short-term biosafety of novel absorbable nano-hydroxyapatite/collagen/poly(lactic acid) composite
Gao Li1, Wang Shuyan1, Wang Rui1, Xu Yonghua1, Gao Jingjing1, Zhang Li2, Liu Wentao2
- 1Department of Pediatric Dentistry, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, Henan Province, China; 2School of Material Science and Engineering, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, Henan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
纳米羟基磷灰石/胶原/聚乳酸复合材料:聚乳酸是一类可降解的高分子生物材料,具有良好的生物相容性、生物可降解性、无毒副作用、易加工成型,且降解产物能参与到人体的新陈代谢,但强度差,在降解过程中产酸易引起周围组织无菌性炎症,且X射线下不显影;纳米羟基磷灰石/胶原是具有模仿天然骨组成成分和分级结构特征的复合体,具有良好的生物活性和骨传导性,且无毒无免疫原性,但其脆性大,不易成型;两者的复合可提高纳米羟基磷灰石/胶原/聚乳酸复合材料的相关性能,但其生物相容性和安全性还需深入探究。
生物安全性:是评价一种新生物材料性质的重要指标之一,是生物材料在临床应用之前必须进行的关键环节,是指材料与人体之间相互作用下必须对人体无毒性、无致敏性、无刺激性、无遗传毒性、无致癌性,对人体组织、血液、免疫系统无不良反应。
背景:课题组前期制备出具有良好生物活性的纳米羟基磷灰石/胶原/聚乳酸[nano-hydroxyapatite/ collagen/poly(L-lactic)acid,nHAC/PLA]复合材料。
目的:评估纳米羟基磷灰石/胶原/聚乳酸材料的生物安全性。
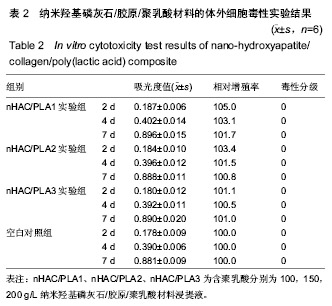
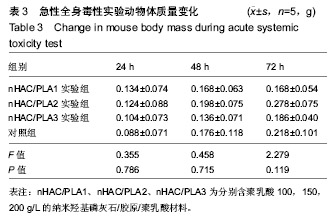
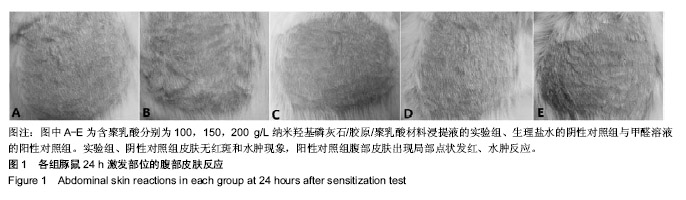
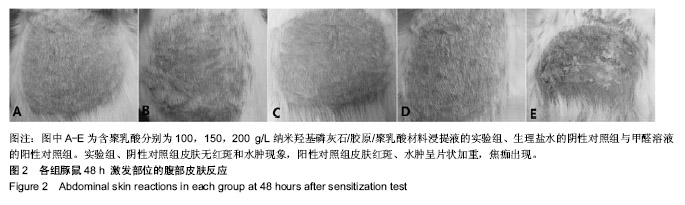
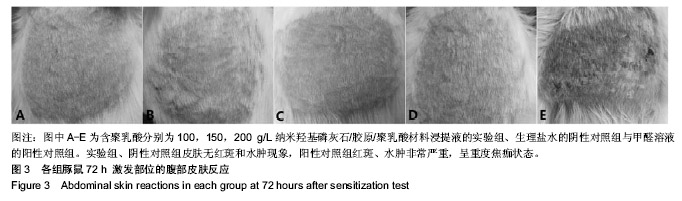
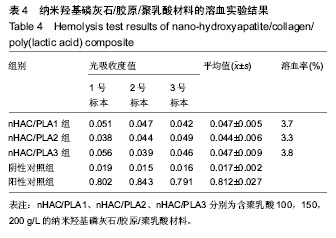
方法:取含聚乳酸分别为100,150,200 g/L的nHAC/PLA材料,制备浸提液,分别记为nHAC/PLA1、nHAC/PLA2、nHAC/PLA3。①细胞毒性实验:采用nHAC/PLA1、nHAC/PLA2、nHAC/PLA3浸提液、细胞培养基培养L929 细胞,采用MTT比色法评价材料的细胞毒性;②急性全身毒性实验:取C57小鼠(郑州大学动物实验中心提供),尾静脉分别注射nHAC/PLA1、nHAC/PLA2、nHAC/PLA3浸提液与生理盐水,注射后24,48,72 h,观察动物一般情况及体质量变化;③血清毒性实验:取SD大鼠(郑州大学动物实验中心提供),分别胃饲nHAC/PLA1、nHAC/PLA2、nHAC/PLA3浸提液与生理盐水,7 d后,采用酶联免疫法检测大鼠血清中白细胞介素1蛋白水平;④致敏实验:将25只白色豚鼠(郑州大学动物实验中心提供)随机分为5组:实验组采用nHAC/PLA1、nHAC/PLA2、nHAC/PLA3浸提液,阴性对照组采用生理盐水,阳性对照组采用体积分数5%甲醛溶液,经过皮内诱导、局部诱导和激发阶段后24,48,72 h,观察各组激发部位皮肤情况;⑤溶血实验:向nHAC/PLA1、nHAC/PLA2、nHAC/PLA3浸提液、生理盐水、蒸馏水中分别加入兔抗凝血,检测溶血率。实验方案经郑州大学伦理委员会审查批准。
结果与结论:纳米羟基磷灰石/胶原/聚乳酸材料的体外细胞毒性为 0 级,急性全身毒性、血清毒性、致敏性和溶血实验结果均为阴性,表明纳米羟基磷灰石/胶原/聚乳酸材料均具有良好的生物安全性。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)